zinc
Showing all 8 resultsSorted by latest
Now Zinc Glycinate
SKU:
098765432345-1
Original price was: 3,100.00৳ .2,999.00৳ Current price is: 2,999.00৳ .
Nature’s Bounty Zinc
SKU:
36849784
Original price was: 1,449.00৳ .1,350.00৳ Current price is: 1,350.00৳ .
Swisse Ultiboost Zinc+ Tablets
SKU:
Swisse123Zinc+
Original price was: 2,600.00৳ .2,440.00৳ Current price is: 2,440.00৳ .
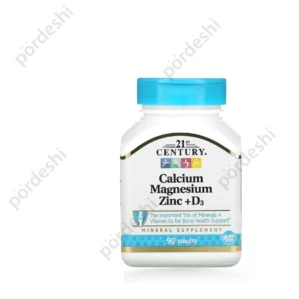
21st Century Calcium Magnesium Zinc Plus D3
SKU:
23456664
Original price was: 1,800.00৳ .1,749.00৳ Current price is: 1,749.00৳ .
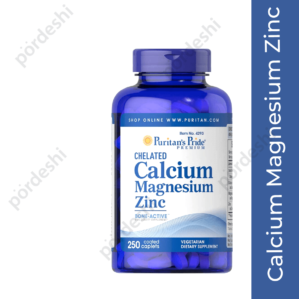
Natures Bounty Calcium Magnesium Zinc in BD
SKU:
2347623874
Original price was: 1,700.00৳ .1,599.00৳ Current price is: 1,599.00৳ .
Zinc Supplements: A Vital Mineral for Health in Bangladesh
Zinc supplement is an essential trace mineral critical to maintaining optimal health. It occurs naturally in various foods and is also available as a dietary supplement. Zinc is indispensable for immune function, wound healing, cellular growth, and cognitive processes. This document examines the health benefits, dietary sources, and risks associated with zinc deficiency and toxicity, with particular emphasis on Bangladesh.
What is Zinc?
Zinc is a vital mineral and antioxidant present in foods such as meats, seafood, beans, and whole grains. Although required only in trace amounts, zinc provides significant health benefits, particularly for immune function, reproductive health, & the maintenance of skin, hair, and nails. Because endogenous zinc synthesis does not occur, adequate dietary intake or supplementation is necessary to meet physiological requirements.
Health Benefits of Zinc
Zinc confers multiple health benefits, supporting immune function, metabolism, and cognitive abilities. The following sections outline the principal health benefits of zinc, with particular relevance to Bangladesh’s population.
1. Immune System Support
Maintaining adequate zinc levels is essential for a strong immune system. Zinc plays a key role in supporting immune cell function and boosting the body’s ability to fight off infections. A zinc deficiency can increase vulnerability to illnesses like pneumonia and diarrhea, which are significant health challenges in Bangladesh.
2. Wound Healing
Zinc accelerates the healing of wounds, cuts, and burns by supporting cell division and tissue growth. Individuals in Bangladesh with chronic wounds, ulcers, or skin conditions may benefit from zinc supplementation to facilitate recovery.
3. Antioxidant Protection
Zinc exhibits antioxidant properties that protect cells from oxidative stress, a factor associated with chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. With the rising prevalence of metabolic diseases in Bangladesh, adequate zinc intake may help mitigate these health challenges.
4. Cognitive Function and Neurological Health
Research indicates that zinc is essential for brain function and may help prevent cognitive decline. In Bangladesh, where the incidence of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease is increasing, zinc’s neuroprotective properties could contribute to reducing the risk of these conditions.
5. Skin Health
Zinc supports skin health and is used in the management of conditions such as acne, eczema, and dermatitis. In Bangladesh, where skin health concerns are prevalent due to environmental factors, zinc intake may improve dermatological outcomes.
6. Sexual Health
Zinc is essential for sperm production and male reproductive health. Zinc deficiency can result in fertility issues and hormonal imbalances. Ensuring adequate zinc levels may benefit men in Bangladesh experiencing reproductive health concerns.
7. Bone Health and Osteoporosis Prevention
Zinc contributes to bone formation and mineralization, which are essential for maintaining bone strength. Evidence suggests that zinc intake can help prevent osteoporosis, a condition characterized by reduced bone density in older adults. As the population in Bangladesh ages, zinc intake becomes increasingly important for bone health.
8. Type 2 Diabetes Management
Individuals with type 2 diabetes frequently exhibit low zinc levels. Zinc supplementation may assist in regulating blood glucose and improving insulin sensitivity. With increasing diabetes prevalence in Bangladesh, particularly among older adults, zinc supplementation may support disease management.
How Much Zinc Should You Take?
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for zinc depends on age, gender, and health status. The following are general guidelines for zinc intake:
- Children (1-3 years): 3 mg/day
- Children (4-8 years): 5 mg/day
- Children (9-13 years): 8 mg/day
- Adolescents (14-18 years): 11 mg (males), 9 mg (females)
- Adults (19 years and older): 11 mg (males), 8 mg (females)
- Pregnant women: 11 mg/day
- Breastfeeding women: 12 mg/day
Primary dietary sources of zinc include seafood, meats, legumes, and nuts. Individuals with dietary restrictions, such as vegetarians in Bangladesh, may require supplementation to achieve recommended intake levels.
Zinc-Rich Foods in Bangladesh
Zinc is present in both animal-based and plant-based foods. The following are key dietary sources of zinc commonly consumed in Bangladesh:
1. Seafood (Fish, Oysters, Shrimp)
Seafoods are among the richest sources of zinc. Fish such as tuna, sardines, and hilsa, which are widely consumed in Bangladesh, provide substantial amounts of bioavailable zinc. Oysters are particularly high in zinc content.
2. Meat (Beef, Chicken, Goat)
Lean meats, including beef, chicken, and goat, are excellent sources of zinc. These meats are dietary staples in Bangladesh and contribute significantly to daily zinc intake.
3. Legumes (Lentils, Chickpeas)
Lentils, chickpeas, and other legumes are important plant-based sources of zinc. These foods are commonly incorporated into Bangladeshi cuisine and are especially beneficial for individuals following vegetarian diets.
4. Whole Grains (Rice, Oats,
Wheat)
Rice, whole wheat bread, and oats are staple foods in Bangladesh that provide moderate amounts of zinc. However, zinc from plant-based sources is less bioavailable than that from animal-based foods.
5. Nuts and Seeds (Almonds, Cashews)
Almonds and cashews are significant sources of zinc, & can be incorporated into the daily diet as snacks or ingredients in various dishes.
6. Dairy (Milk, Yogurt)
Milk and yogurt supply moderate amounts of zinc, contributing to daily requirements, particularly for children and older adults.
Zinc Deficiency in Bangladesh: Signs and Risks
Zinc deficiency is prevalent in regions with inadequate dietary intake of zinc-rich foods. In Bangladesh, where food insecurity and malnutrition are widespread, particularly in rural areas, zinc deficiency can result in significant health consequences.
Signs of Zinc Deficiency:
- Delayed growth and development in children
- Loss of appetite
- Weakened immune function, leading to frequent infections
- Hair loss and skin conditions (e.g., eczema, acne)
- Diarrhea
- Impaired wound healing
Zinc deficiency can result in severe outcomes, including Keshan disease, a form of heart disease, and Kashin-Beck disease, a type of osteoarthritis. These conditions are more prevalent in areas with low zinc intake.
Zinc Toxicity: The Risks of Overuse
Although zinc is essential for health, excessive intake may result in toxicity. The tolerable upper intake level for zinc supplementation in adults is 40 mg per day. Exceeding this threshold can cause adverse effects, including:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of appetite.
- Abdominal pain.
- Diarrhea.
- Reduced immune function
- Disruption of copper absorption
Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended before initiating zinc supplementation, particularly for pregnant or breastfeeding women and individuals with chronic health conditions.
Conclusion: Zinc for Optimal Health in Bangladesh
This mineral supports immune function, skin integrity, and reproductive health. In Bangladesh, where malnutrition and zinc deficiency are significant public health concerns, adequate zinc intake is vital. Consuming zinc-rich foods, such as seafood, meat, lentils, and nuts, enables individuals to meet daily nutritional requirements.
Individuals at risk of zinc deficiency may require supplementation under medical supervision. Excessive zinc intake should be avoided because of potential adverse health effects. Maintaining a balanced diet and awareness of zinc’s role can promote optimal health in Bangladesh.



 Oral Care
Oral Care Sports Nutrition
Sports Nutrition