Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Showing all 8 resultsSorted by latest
Nutricost Niacinamide
SKU:
2454521
Original price was: 3,100.00৳ .2,999.00৳ Current price is: 2,999.00৳ .
21st Century Niacinamide
SKU:
2343444-1-1
Original price was: 2,500.00৳ .2,345.00৳ Current price is: 2,345.00৳ .
Puritan’s Pride Niacin
SKU:
9865434567
Original price was: 3,150.00৳ .2,849.00৳ Current price is: 2,849.00৳ .
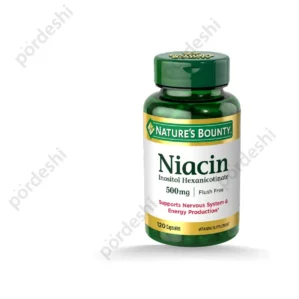
Nature’s Bounty Niacin
SKU:
12555
Original price was: 3,150.00৳ .2,849.00৳ Current price is: 2,849.00৳ .
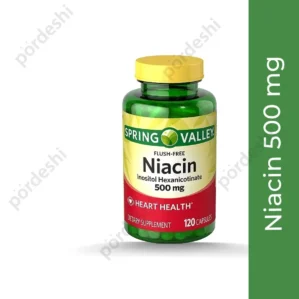
Spring Valley Niacin 500mg
SKU:
654555
Original price was: 3,150.00৳ .2,849.00৳ Current price is: 2,849.00৳ .
Now Niacin 500mg
SKU:
32849687236
Original price was: 2,600.00৳ .2,450.00৳ Current price is: 2,450.00৳ .
Niacinamide Supplements: Comprehensive Guide to Benefits, Uses, and Safety
Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide, is a potent form of Vitamin B3 that has gained popularity in skincare and nutritional supplements. In Bangladesh, growing awareness of skincare and health supplementation has led to increased interest in niacinamide supplements for their diverse health benefits, including promoting skin health and preventing deficiency-related conditions. This guide provides a detailed overview of the key benefits, food sources, uses, side effects, and safety considerations of niacinamide supplements, with a focus on their relevance in Bangladesh.
What is Niacinamide (Nicotinamide)?
Niacinamide is a water-soluble form of vitamin B3, distinct from nicotinic acid (niacin). While both compounds offer health benefits, niacinamide is often preferred in supplements due to its greater tolerability and efficacy. In Bangladesh, niacinamide is increasingly incorporated into dietary supplements and topical skincare products designed to support overall health.
Benefits of Niacinamide Supplements
Niacinamide offers several notable health benefits, making it a popular choice for supplementation, particularly in the management of skin health and the prevention of niacin deficiencies. Key benefits include the following:
- Helps Prevent and Treat Niacin Deficiency
Severe niacin deficiency can lead to pellagra, a condition characterized by skin issues, gastrointestinal symptoms, and neurological effects. Niacinamide supplements are highly effective in preventing and treating this condition without causing the flushing and discomfort that high-dose nicotinic acid might induce. - Promotes Skin Health
Niacinamide is recognized for its skin-rejuvenating properties, including the reduction of hyperpigmentation, fine lines, and redness. Topical application is particularly beneficial for individuals with acne, as vitamin B3 helps regulate sebum production and decrease inflammation. Oral supplementation can complement topical regimens, supporting a healthy and radiant complexion. - Reduces Risk of Skin Cancer
Niacinamide may help reduce the risk of certain types of skin cancer, especially basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, in individuals at higher risk. Its ability to repair DNA damage and enhance immune function contributes to this protective effect. - Supports Joint Health
Preliminary studies indicate that niacinamide may contribute to improved joint health by reducing inflammation. In individuals with osteoarthritis, niacinamide has been associated with symptom relief and enhanced mobility. - Regulates Phosphorus Levels in the Body
Niacinamide may serve as a therapeutic option for managing hyperphosphatemia, or elevated phosphorus levels in the blood, particularly among individuals undergoing dialysis. This action supports proper mineral balance, which is essential for kidney health.
Food Sources of Niacinamide
Although niacinamide is available as a supplement, it is also found in a variety of foods. Incorporating niacin-rich foods into the diet can naturally increase niacinamide levels. In Bangladesh, common dietary sources include the following:
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey are excellent sources of niacin.
- Fish: Tuna and salmon provide substantial amounts of niacinamide.
- Nuts and Seeds: Peanuts, almonds, and flaxseeds contribute to niacin intake.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats, and wheat are common in Bangladeshi cuisine and are good sources.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and beans are rich in niacin.
- Vegetables: Potatoes and green leafy vegetables like spinach also contain niacinamide.
Inclusion of these foods in a balanced diet helps prevent niacin deficiency and supports overall health.
How to Take Niacinamide Supplements
Niacinamide supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, powders, and topical creams. Oral supplements are best taken with food to minimize the risk of gastrointestinal discomfort. For topical use, lotions or serums can be applied directly to the skin.
The typical dosage of niacinamide supplements is approximately 300 mg per day; however, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dose, particularly when addressing specific health concerns such as skin conditions or hyperphosphatemia.
Recommended Dosage and Safety Guidelines
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for niacin varies by age, sex, and life stage. Here is a general breakdown:
- Infants (0-6 months): 2 mg/day
- Children (1-3 years): 6 mg/day
- Adolescents (14+ years): 14-16 mg/day
- Pregnant women: 18 mg/day
- Lactating women: 17 mg/day
Caution is advised when using niacinamide supplements in individuals with liver disorders or a history of stomach ulcers. Niacinamide is generally safe within recommended limits, but high doses (over 3 grams per day) may result in side effects such as nausea, headache, dizziness, or skin rashes.
Possible Side Effects and Interactions
Niacinamide is considered safe for most individuals when used as directed. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects, including the following:
- Stomach upset or nausea.
- Dizziness or headache
- Skin irritation (for topical use)
Consultation with a healthcare provider is strongly recommended before initiating niacinamide supplementation, particularly for individuals taking anticoagulants or certain antiepileptic medications such as carbamazepine. Niacinamide may alter the effectiveness of these medications when used concurrently.
Niacinamide vs. Niacin (Nicotinic Acid)
Both niacinamide and niacin (nicotinic acid) are forms of Vitamin B3; however, niacinamide does not cause the skin flushing or discomfort associated with high doses of niacin. As a result, niacinamide is the preferred form for supplementation, especially for individuals seeking skin health benefits without the adverse effects linked to high-dose niacin.
Why Choose Niacinamide Supplements in Bangladesh?
In Bangladesh, where skin-related concerns such as pigmentation, acne, and sun damage are prevalent, niacinamide supplements may provide a safe and effective solution. With a broad range of benefits, including improved skin texture and support for metabolic functions, niacinamide supplementation can contribute to enhanced skin health and overall wellness. Incorporating these supplements into a daily routine may complement a balanced diet and skincare regimen, resulting in visible improvements over time.
Conclusion
Niacinamide supplements serve as an effective means of promoting skin health, preventing deficiencies, and supporting various physiological functions. From treating acne to reducing the risk of skin cancer, niacinamide provides a wide range of benefits for individuals in Bangladesh. For those seeking to improve skin appearance or manage specific health conditions, niacinamide may be a valuable addition to a daily regimen. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential to ensure safe and effective use of niacinamide supplements.
References:
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements – Niacinamide NIH
- Healthline: Niacinamide for Skin Health Healthline
- Mayo Clinic: Niacinamide and Skin Care Mayo Clinic
- PubMed Central: The Benefits of Niacinamide in Dermatology PMC



 Oral Care
Oral Care Sports Nutrition
Sports Nutrition