Vitamin B9 (Folate - Folic Acid)
Showing all 2 resultsSorted by latest
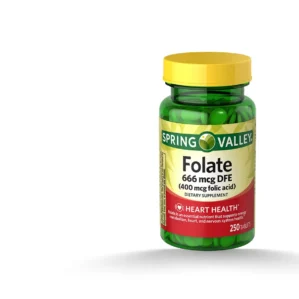
Spring Valley Folate
Folic Acid: Essential Vitamin B9 for Optimal Health in Bangladesh
What is Folic Acid?
Key Health Benefits of Folic Acid
-
Neural Tube Defect Prevention:
A primary benefit of folic acid is its capacity to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs) in developing fetuses. Evidence indicates that sufficient folic acid intake before and during early pregnancy significantly decreases the incidence of conditions such as spina bifida and anencephaly. Health organizations globally, including those in Bangladesh, recommend that women of childbearing age consume a daily supplement of 400 micrograms of folic acid to prevent these serious birth defects.
-
Promoting Healthy Pregnancy:
In addition to preventing neural tube defects, folic acid supports normal fetal development by reducing the risk of premature birth and low birth weight. Research indicates that maternal folate supplementation enhances placental function and fetal growth. Given the high prevalence of underweight births and maternal malnutrition, adequate folic acid intake during pregnancy is particularly critical.
-
Support for Red Blood Cell Production:
Folic acid is required for healthy red blood cell production. Deficiency can cause megaloblastic anemia, leading to fatigue, weakness, pallor, and shortness of breath. Since anemia is common in Bangladesh, adequate folate intake is important to help address this issue.
-
Heart Health:
Folate is involved in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid associated with increased cardiovascular disease risk when present at elevated levels. Folic acid supplementation can reduce homocysteine concentrations, thereby lowering the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular conditions. These risks are increasing among older adults, highlighting the potential benefit of folic acid supplementation.
-
Mental Health and Cognitive Function:
Folate deficiency is associated with an increased risk of depression and cognitive decline. Adequate folate is required for the synthesis of serotonin, a neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation. Evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation may alleviate symptoms of depression, particularly when combined with other B vitamins such as B12. This is especially relevant in Bangladesh, where mental health disorders frequently remain undiagnosed or untreated.
Folic Acid Deficiency in Bangladesh
- Neural tube defects in newborns.
- Impaired DNA synthesis affects cell division and growth.
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Sources of Folic Acid
- Leafy greens (spinach, mustard greens)
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, beans)
- Fruits (oranges, bananas, avocados)
- Whole grains (brown rice, oats)
- Fortified cereals and bread
The Role of Folic Acid Fortification:
Recommended Dosages for Folic Acid
- Adults: 400 micrograms
- Pregnant women: 600 micrograms
- Women planning to conceive: 400 micrograms daily
- Children: Varies from 150 to 400 micrograms depending on age
Conclusion
Key Takeaways:
- Folic acid is vital for DNA synthesis, red blood cell production, and heart health.
- It is particularly important for pregnant women to prevent neural tube defects in babies.
- Folic acid fortification programs are key in reducing deficiency and improving public health outcomes.
References:
- Crider, K. S., Cordero, A. M., Qi, Y. P., et al. (2013). Prenatal folic acid and risk of birth defects in children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- De Wals, P., Tairou, F., Van Allen, M. I., et al. (2007). Reduction in neural-tube defects after folic acid fortification in Canada. The New England Journal of Medicine.
- National Institutes of Health (2023). Folate: Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. Retrieved from NIH Website.



 Oral Care
Oral Care Sports Nutrition
Sports Nutrition